Am I an Addict? Quiz
If you’ve ever wondered, “Am I an addict?” you’re not alone. According to a survey in 2020 by the National Center for Drug Abuse Statistics, 59.277 million people aged 12 and above have used illegal drugs or misused prescription drugs within the last year. With rising rates of overdose-related deaths each year, this issue is more pressing than ever.
Identifying addiction is a complex process, and understanding the nuances between casual drug use, dependency, and addiction isn’t always easy. Acknowledging the question, “Do I have an issue?” is a courageous and pivotal step toward healing.
Self-Assessment: Am I an Addict?
If you’re asking yourself whether or not you have an addiction problem, you’re not alone. To complement our addiction treatment programs at Profound Treatment, we have designed a tool to help empower you to ask yourself difficult questions. The following quiz is designed to provide you with a clearer perspective on your or a loved one’s drug use to assist in determining if it’s time to seek professional help. The quiz utilizes the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) criteria for diagnosing substance use disorders. It is important to note that the DSM-5 criteria for substance use disorders are based on a spectrum, ranging from mild to severe, depending on the number of diagnostic criteria met by an individual.
Visit our get help now pages to find support for yourself or a loved one.
Contact Profound Treatment to Learn More
Our team is standing by to discuss treatment options with you. Your call is completely confidential and no obligation is required.
What is Addiction?
Addiction is a complex, chronic disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use, despite harmful consequences. It is a brain disorder that involves a deep-rooted craving for a substance or behavior, leading to an inability to control its use. Addiction refers to a condition where there is a psychological and/or physical dependence on alcohol or drugs. It is also frequently synonymous with substance dependence and can extend to behavioral disorders, including addictions like gambling, sexual activities, and technology or internet use.
When thinking about addiction or substance use disorder (SUD), It can be important to understand the difference between addiction and substance use or abuse. According to the American Psychological Association, substance abuse is characterized by a habitual pattern of using substances in a way that leads to negative consequences in various aspects of life. This may include repeated problems in social and personal relationships, legal issues, and interpersonal conflicts.
How Does Addiction Affect the Brain?
Addiction fundamentally affects the brain’s function, particularly its reward system. Substances or behaviors that lead to addiction can alter brain chemistry, changing how we experience pleasure. As a result, other activities may seem less enjoyable. This change can trap individuals in a cycle of needing higher quantities of a chosen substance or behavior to feel the same level of happiness or relief, a phenomenon known as tolerance.
Beyond the physical, addiction has a psychological dimension. It often becomes a way to escape stress or emotional discomfort, providing temporary relief or a sense of euphoria. However, this relief is usually short-lived and followed by a ‘crash’ or withdrawal symptoms, prompting even more use of the addictive substance or behavior.
7 Signs of Addiction
Recognizing addiction is vital for timely intervention and effective treatment. Often, the shift from casual use to dependency is subtle and gradual, making it difficult to identify. Understanding the early signs of addictive behavior is an essential step for anyone concerned about their own behavior or that of a loved one.
- Cravings and compulsive use: One of the most evident signs of addiction is the intense craving for a substance or behavior. This craving often leads to compulsive use, where the individual feels an overwhelming need to use the substance or engage in the behavior despite knowing the negative consequences.
- Loss of control: Individuals struggling with addiction may find it difficult to control their use. They might consume more of the substance or spend more time engaging in the behavior than intended and often fail to cut down or stop.
- Tolerance: Over time, a person with an addiction may require larger amounts of the substance to achieve the same effect. This physiological response is known as tolerance. Through this process, the body adjusts to the chosen substance, diminishing its impact over repeated use.
- Withdrawal symptoms: When not using the substance or engaging in the behavior, individuals may experience withdrawal symptoms. These can be physical (such as headaches, nausea, shaking) or psychological (such as anxiety, irritability, or depression).
- Neglecting responsibilities: Addiction often leads to neglect of personal, professional, or educational responsibilities. Individuals may start performing poorly at work or school or neglect household duties and personal relationships.
- Continued use despite negative consequences: Even when facing serious consequences like health problems, financial issues, or damaged relationships, individuals with an addiction may continue their substance use or behavior, indicating a loss of control over their actions.
- Social and recreational sacrifices: People suffering from addiction might give up important social, occupational, or recreational activities. They may withdraw from hobbies, sports, and social events they once enjoyed to spend more time obtaining, using, or recovering from the effects of the substance or behavior.
If you or someone you know is exhibiting these signs, seeking professional help is a critical first step towards recovery. Contact Profound Treatment today to speak with one of our experienced team members. We’re here to support you each step of the way. Call (310) 929-9546.
Causes of Addiction or Substance Use Disorder (SUD)
The question of whether addiction is genetic has been a subject of extensive research and debate. Studies suggest that genetics can play a significant role in the likelihood of developing an addiction, though it’s not the sole factor.
- Genetic factors in addiction: Scientific research indicates that certain genetic predispositions can increase an individual’s susceptibility to addiction. Genes can influence how a person reacts to a substance, how addictive a substance is to them, and even how easy or difficult it is for them to quit. Estimates suggest that genetics can account for approximately 40% to 60% of the risk for addiction.
- Family history: A family history of addiction can be a strong indicator of genetic risk. If close family members have struggled with addiction, it may suggest a genetic predisposition. A family history of addiction does not, however, guarantee that someone will develop an addiction themselves. It simply indicates a higher risk factor.
- Environmental factors: While genetics can increase the risk of addiction, environmental factors often trigger its onset. These factors include peer pressure, availability of substances, stress, and traumatic experiences. The interaction between genetic predisposition and environmental influences is complex and significant regarding the likelihood of developing a SUD.
- Behavioral and substance addictions: Genetic predisposition is not limited to substance addiction (like drugs or alcohol) but can also extend to behavioral addictions (such as gambling or internet addiction). Research suggests that certain genetic traits may predispose individuals to a range of addictive behaviors.
- Implications for treatment and prevention: Understanding the genetic aspect of addiction can have significant implications for treatment and prevention. It can lead to more personalized treatment approaches, recognizing each individual’s genetic makeup. Additionally, awareness of a genetic predisposition can be a key factor in prevention strategies, particularly for younger individuals with a family history of addiction.
While genetics play a crucial role in the risk of developing an addiction or substance use disorder (SUD), they are part of a broader picture that includes environmental and personal factors. This multifaceted nature of addiction underscores the need for comprehensive treatment approaches that address all underlying causes, both genetic and environmental.
Overcoming Addiction
Deciding to seek help for addiction is a pivotal moment in anyone’s journey toward recovery. Acknowledging that you need support to overcome the challenges of addiction is a courageous step. This decision often comes after a period of reflection followed by the difficult realization that addiction is affecting various aspects of your life, including health, relationships, and happiness.
At Profound Treatment, we believe overcoming addiction is formidable but filled with hope and possibility. It’s a path that requires commitment, support, and often, professional intervention. Understanding the complexities of this journey, our experienced team of professionals is committed to guiding you through every step of the way.
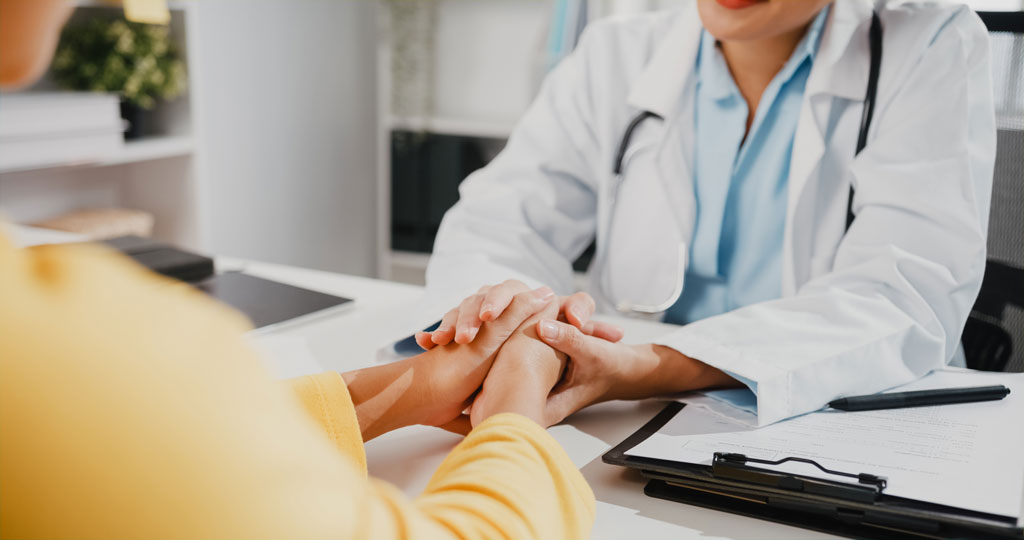

Why Choose Profound Treatment?
Profound Treatment’s specialized substance abuse programs stand out for a number of reasons. Offering a full continuum of care, our serene setting in Woodland Hills provides a tranquil environment conducive to recovery at each phase of the journey.
Personalized Care
We understand that every individual’s journey with addiction is unique. Our treatment plans are tailored to meet your needs, ensuring the most effective approach to your recovery.
Expert and compassionate staff
Our team comprises experienced professionals who are not only experts in their fields but also deeply compassionate. They provide a supportive and understanding environment that fosters healing.
Holistic approach to recovery
We believe in treating the whole person, not just the addiction. Our programs include a range of therapeutic modalities, lifestyle coaching, and wellness activities like equine and experiential therapy that support overall health and well-being.
Community and support:
At Profound Treatment, you become part of a supportive community. We offer group therapies and support networks that provide encouragement and understanding from others on similar paths.
Begin Healing with Profound Today
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. At Profound Treatment, we offer the care, support, and guidance you need to overcome addiction and build a healthier, happier future. If you or a loved one is struggling with addiction, we encourage you to take the first step toward recovery by reaching out to us today. Call (310) 929-9546 or visit our website to verify your insurance.
FAQ's
1. What are the first signs of addiction?
The first signs that an individual might be addicted to a substance include increased tolerance, cravings, neglecting responsibilities, changes in behavior, and withdrawal symptoms when not using the substance.
2. Can addiction be cured?
Addiction is generally considered a treatable condition, not curable. Long-term management and recovery are possible with appropriate treatment and support.
3. How do I approach a loved one I suspect is struggling with addiction?
Approach them with compassion and understanding. Avoid judgment or confrontation. Express your concerns calmly and encourage them to seek professional help. If you need support with this vital step, visit our website for more information about getting help for a loved one or contact us today by calling (310) 929-9546.
Click here to read more about how to help a loved one or family member with addiction.
4. What role does mental health play in addiction?
Mental health is closely linked to addiction. Many individuals with addiction issues also suffer from mental health disorders, and vice versa. Addressing both is crucial in treatment, so Profound Treatment offers dual-diagnosis treatment.
5. What is the essential feature of drug addiction?
The essential feature of drug addiction is a persistent pattern of drug use causing significant impairment or distress, including health problems, disability, and failure to meet responsibilities.
6. What or who is considered an addict?
Someone who identifies as an addict typically cannot control their use of substances or behaviors and continues using them despite harmful consequences.
7. What is the process for identifying, assessing, and diagnosing clients for addictive disorders?
The process involves a thorough evaluation, including medical history, psychological assessment, and substance use patterns, often using criteria from the DSM-5 or similar diagnostic tools.
Licensed by the State Department of Health Care Services.
Profound Healing Centers License No: 191092BP Exp. 5/31/26 (current/active)
Profound Healing Centers License No: 191092AP Exp. 7/31/25 (current/active)
Profound Treatment License No: 191047CP Exp. 1/31/27 (current/active)
Profound Treatment License No: 191047AP Exp. 8/31/26 (current/active)
Profound Treatment License No: 191047EP Exp: 3/31/26 (current/active)
Profound Treatment License No: 191047DP Exp. 9/30/25 (current/active)
Click here for more information about DHCS licensing.
| Start your healing today>> | |
|---|---|
| (310) 929-9546 |