Addiction is a complex condition often emanating from various underlying factors, one of the most significant being childhood trauma. At Profound Treatment in Woodland Hills, Los Angeles, California, we specialize in providing comprehensive dual diagnosis treatment for individuals grappling with addiction and other mental health issues like trauma. We understand the intricate link between substance use and trauma is crucial and ensure individuals in our programs receive the support and therapy needed to heal from their past and move towards a healthier future.
Learn More About Our Trauma Treatment Program
The Connection Between Addiction and Childhood Trauma
Childhood trauma encompasses a wide range of distressing experiences, including physical, emotional, and sexual abuse, neglect, and exposure to violence. These traumatic events can have profound and lasting effects on an individual’s mental and emotional well-being, often serving as a significant risk factor for developing substance abuse disorders later in life.
Research consistently indicates that individuals who have experienced childhood trauma are at a higher risk of turning to drugs or alcohol as a coping mechanism. This behavior often stems from an attempt to numb the psychological discomfort and distress associated with past traumatic experiences events.
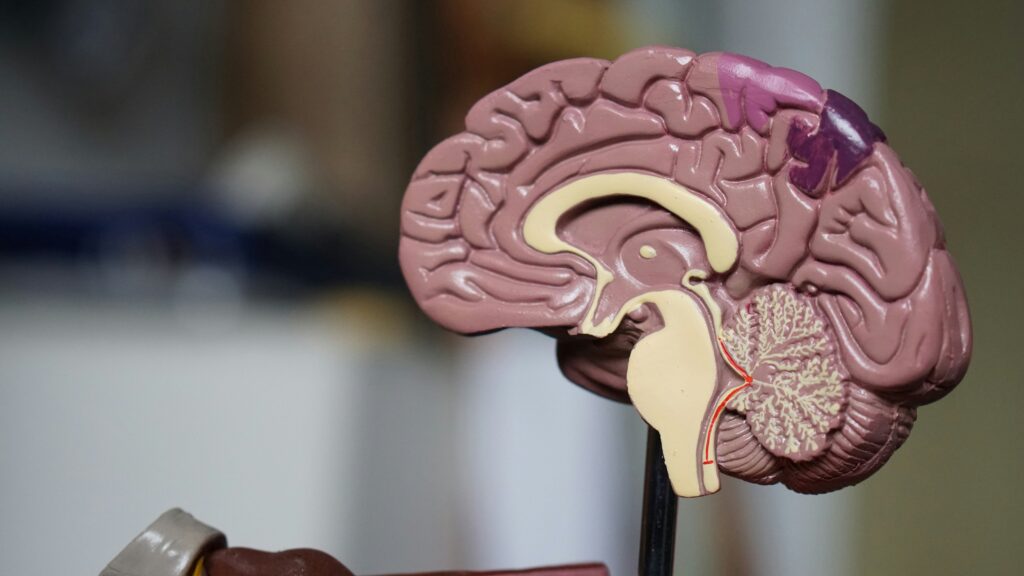
The Impact of Trauma on the Brain
Traumatic events, especially during the crucial developmental stages of childhood, can significantly impact brain development. The brain’s response to trauma involves the release of stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline. When these stress responses are triggered frequently or intensely, they can alter the brain’s structure and function.
These alterations can particularly affect brain areas responsible for emotional regulation, impulse control, and reward processing. Some examples include:
- The amygdala, which processes emotions, may become overactive, leading to heightened anxiety and emotional instability.
- The prefrontal cortex, which is involved in decision-making and impulse control, may become underactive, reducing an individual’s ability to resist the urge to engage in substance use.
These neurological changes and any related PTSD symptoms can make individuals more susceptible to addiction, as they may seek out drugs or alcohol to self-medicate and manage overwhelming emotions or distress.
Recognizing the Signs of Childhood Trauma in Addiction
Understanding the signs of childhood trauma in those struggling with addiction is paramount for ensuring the most exhaustive, effective approach to treatment. For individuals who have experienced significant trauma, either as adults or children, treatment is most effective when it takes into consideration both substance use and any underlying issues or co-occurring conditions, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Trauma-related symptoms can manifest in various ways, influencing both psychological and physical health and even impacting treatment for substance use disorders (SUDs) in some ways. Common indicators of childhood trauma in those battling addiction include:
- Emotional instability: Individuals may have difficulty regulating their emotions, experiencing frequent mood swings and heightened levels of anxiety or depression. This emotional volatility often reflects the unresolved trauma from their past.
- Relationship issues: Forming and maintaining healthy relationships can be challenging for those with a history of traumatic experiences. These individuals often exhibit trust issues and attachment problems, finding it difficult to build and sustain close connections with others.
- Behavioral problems: Engaging in risky behaviors, including substance abuse, can be a way for some individuals to cope with unresolved trauma. This maladaptive coping mechanism is often a sign that the person lacks healthy coping skills and is struggling to manage their emotional pain and distress.
- Physical symptoms: Trauma can also manifest physically, leading to unexplained chronic pain, gastrointestinal issues, and other psychosomatic symptoms. These physical manifestations are often linked to the body’s response to ongoing psychological stress and unresolved trauma.
Recognizing these signs may be the first step towards getting help for addiction and unresolved trauma. Effective treatment requires addressing both the substance use and the underlying trauma, healing the whole person rather than just their symptoms.

If you or a loved one is struggling with unresolved trauma and substance use, Profound Treatment offers a sanctuary for healing and expansion. Contact us today to learn how we can support you on the journey to recreate your life.
The Role of Dual Diagnosis in Treating Addiction and Trauma
At Profound Treatment, we know from experience that many people struggling with addiction addiction also have co-occurring mental health disorders, such as PTSD, anxiety, depression, or bipolar disorder. When a dual diagnosis is present, it requires an integrated treatment approach that addresses both the addiction and the underlying trauma. This sets the stage for profound, lasting change beyond detox and residential treatment.
Integrated Treatment Approach
Our integrated treatment approach at Profound in Woodland Hills combines evidence-based therapies with holistic practices to ensure comprehensive care. Some of the most valuable aspects of our treatment programs for individuals struggling with trauma and other co-occurring conditions alongside addiction include:
-
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): CBT helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with both trauma and addiction.
- Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR): EMDR is a specialized therapy designed to help individuals process and integrate traumatic memories, reducing their impact on current functioning.
- Somatic Experiencing Therapy: This therapy focuses on the connection between the mind and body, helping individuals release trauma stored in the body through techniques such as deep breathing, relaxation exercises, and body awareness practices.
- Equine & Animal Therapy: Interacting with animals can provide emotional support and help individuals develop trust, empathy, and responsibility. This therapy is perfect for trauma survivors and is particularly beneficial for those who have difficulty opening up in traditional therapy settings.
- Art & Music Therapy: Creative therapies like art and music therapy allow individuals to express their emotions and experiences non-verbally, facilitating healing and self-discovery.
- Experiential & Adventure Therapy: This approach involves engaging in activities that promote personal growth, self-esteem, and emotional regulation. Activities may include outdoor adventures, team-building exercises, and other experiential learning opportunities.
Creating a Safe and Supportive Environment
Healing from addiction and trauma is a complex process that requires a safe and supportive environment where individuals feel understood and cared for. At Profound Treatment, we prioritize creating a welcoming, supportive, and inclusive atmosphere, ensuring our clients receive the empathy and compassion they need during their recovery journey.
1. Importance of Trust
Building trust is a crucial component of the healing process for both substance abuse and other mental health disorders, including trauma and PTSD. Our dedicated addiction and mental health professionals work tirelessly to establish a trusting relationship with you, fostering a sense of safety and security essential for the best chance at long-lasting recovery.
2. Individualized Treatment Plans
Recognizing that each person’s experience with addiction and trauma is unique, we develop personalized treatment plans tailored to meet each individual’s specific needs. This individualized and tailored approach ensures that you or your loved one receives the most effective therapies and interventions for their distinctive situation.
Crafting Your Path to Recovery
Recovery from addiction and childhood trauma is a challenging journey, but with the proper support and treatment, it is entirely possible. At Profound Treatment, we are committed to helping you or your loved one create and navigate this path, providing the tools and resources to attain lasting sobriety and true emotional healing.
1. Support System
Building a solid support system is vital for long-term recovery. We encourage our clients to engage with family, friends, and support groups, fostering connections that can provide encouragement and personal responsibility. Our programs offer a community atmosphere that encourages peer support and accountability.
2. Relapse Prevention
Our comprehensive treatment programs include aftercare planning and relapse prevention strategies, equipping individuals with the skills to manage triggers and maintain their sobriety post-treatment. We are committed to supporting you or your loved one through each phase of their journey toward a new life, and our support extends beyond the length of our residential programs.
Experience Profound Healing
Understanding the profound connection between addiction and childhood trauma is part of beginning a holistic journey toward healing and long-term wellness. We address these complex issues at Profound Treatment in Woodland Hills, Los Angeles, through a holistic and integrated approach to mental health and addiction treatment. By providing specialized trauma therapy and dual diagnosis treatment programs, alongside personalized treatment plans and a safe, supportive, and inclusive environment, we empower everyone who comes through our doors to heal, let go of the past, and build a brighter future free from addiction.
If you or a loved one is struggling with addiction and trauma-related symptoms, reach out to Profound Treatment. Our compassionate team is here to support you every step of the way on your journey to recovery. Let us help you take the first step towards a healthier, more fulfilling life.
References
- De Bellis, M. D., & Zisk, A. (2014). The biological effects of childhood trauma. Child and adolescent psychiatric clinics of North America, 23(2), 185–vii. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chc.2014.01.002
- Khoury, L., Tang, Y. L., Bradley, B., Cubells, J. F., & Ressler, K. J. (2010). Substance use, childhood traumatic experience, and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder in an urban civilian population. Depression and anxiety, 27(12), 1077–1086. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.20751
- Bremner J. D. (2006). Traumatic stress: effects on the brain. Dialogues in clinical neuroscience, 8(4), 445–461. https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2006.8.4/jbremner
- Woody G. (1996). The Challenge of Dual Diagnosis. Alcohol health and research world, 20(2), 76–80. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6876494/