What Causes Depression and Anxiety?
The Connection Between Depression and Anxiety
Among the most prevalent psychiatric disorders are anxiety and depressive disorders. Anxiety and depression highly co-occur, despite being different mental health conditions. This means a person is more likely to experience the other condition if they have one of the conditions. About 40 to 50 percent of people suffer from both depression and anxiety.
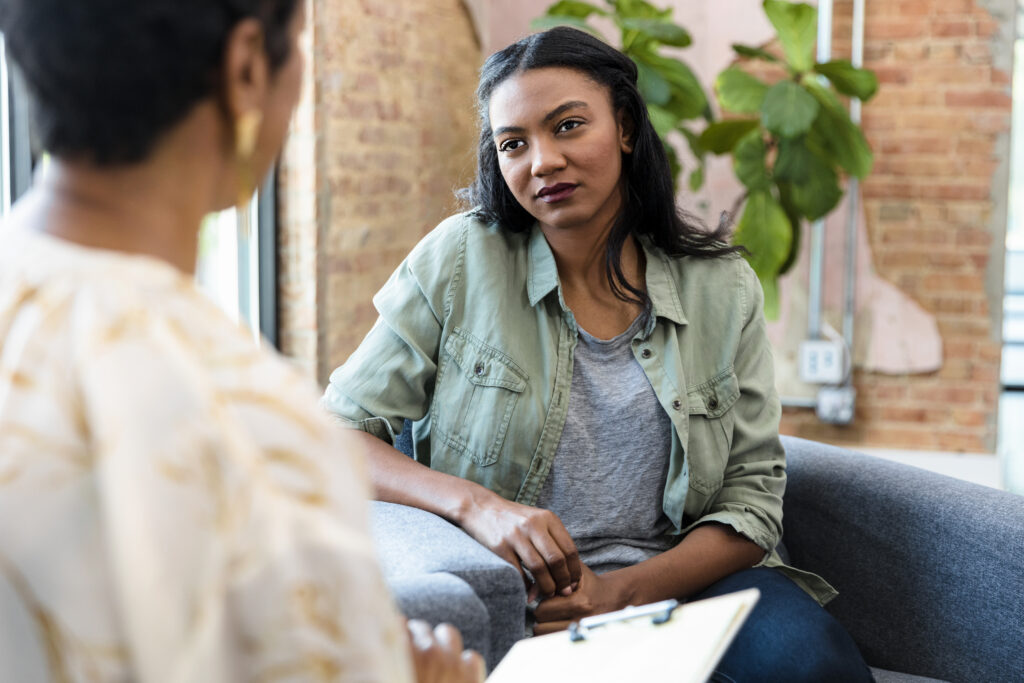

Contact Profound Treatment to Learn More
Our team is standing by to discuss treatment options with you. Your call is completely confidential and no obligation is required.
What is Depression?
What is Anxiety?
Anxiety is the feeling of uneasiness, fear, and dread. The individual’s heart rate may increase, they might start to sweat, and they may feel tense. It can be a typical stress response. However, it could develop into a medical disorder if a person experiences excessive anxiety regularly. Severe anxiety can have a significant negative impact on daily life.
Is Depression Genetic?
What Are the Main Causes of Depression and Anxiety?
Brain Chemistry
Genetics
Life Events
Medical Conditions
Medication
Beta-blockers, hormonal birth control, and certain corticosteroids, among other medicines, can increase the chance of developing depression.
Personality
What Are the Symptoms of Depression and Anxiety?
- Feeling very sad, hopeless, or worried.
- Not enjoying things that used to give you joy.
- Being easily irritated or frustrated.
- Eating too much or too little.
- Changes in how much you sleep.
- Having a difficult time concentrating on things.
Diagnosing Depression and Anxiety
How is Depression Syndrome Diagnosed?
- When did the depression symptoms first start?
- How long the symptoms lasted, and how frequently they happened?
- Do the symptoms prevent the person from going out or engaging in regular activities?
Can Depression Be Prevented?
How Is Anxiety Diagnosed?
Can Anxiety Be Prevented?
- Maintain your physical health by eating a healthy, balanced diet.
- Learn relaxing techniques, including deep diaphragmatic breathing. By practicing relaxation techniques, you can be prepared to handle anxiety.
- You may easily manage and eliminate your anxious thought patterns by being aware of them. Understanding how anxiety impacts your emotions and behaviors and the trigger is the first step toward becoming more aware of it.
How Is Genetics Linked to the Risk of Depression?
Does Depression Often Occur with Grief?
Treatment Options

Therapies for Anxiety
There are several types of anxiety disorders, and the type of therapy a person will receive depends on their diagnosis and how severe the symptoms are. The following are major forms of therapy for anxiety:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): is the most widely used and effective psychotherapy for anxiety disorders. CBT is a short-term therapy that teaches individuals specific techniques to manage their symptoms. CBT effectively manages anxiety symptoms by addressing negative habits and distortions in their perception of the environment and themself.
- Dialectical Behavioral Therapy: Individuals will learn to accept their anxiety while proactively trying to modify it during DBT therapy. The four effective skills that DBT treatment teaches are emotion regulation, mindfulness, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness.
Therapies for Depression
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy: The primary goal of CBT is to change depressive thought patterns and behaviors. Cognitive therapy teaches patients to recognize recurring negative thoughts and behavior patterns and replace them with more positive ones. CBT sessions may involve keeping a journal and practicing relaxation techniques and readings.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy: Individuals can learn to accept their unpleasant feelings, deal with stress, and control their responses during DBT. This treatment uses mindfulness techniques to support crisis coaching, in which the therapist instructs the individual on facing challenging circumstances.
- Psychodynamic Therapy: This treatment method aims to assist the patient in becoming more conscious of their emotions and to help the patient bear these sensations more effectively and put them into a useful perspective. This approach can also aid in the development of self-awareness and the enhancement of specific emotional capacities.
Medication-Assisted Treatment
Medication-assisted treatment (MAT)combines counseling, behavioral therapies, and prescription medication to treat depression and anxiety. MAT involves using antidepressants to treat severe depressive and anxiety disorders.
Support Groups
Get Help for Anxiety and Major Depressive Disorder at Profound Treatment Center
If you or a loved one is experiencing anxiety and depression symptoms, contact Profound Treatment Center in California for a free comprehensive assessment.
Profound Treatment Center accepts most private insurance plans and develops customized research-backed treatment plans based on your unique needs. Book a consultation session with us and begin your journey to recovery and sustainable wellness.
Resources
-
1https://adaa.org/understanding-anxiety/facts-statistics
-
2https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/statistics/major-depression#:~:text=collection%20in%202020.-,Major%20Depressive%20Episode%20with%20Impairment%20Among%20Adults,6.0%25%20of%20all%20U.S.%20adults
-
3https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/campaign/tips/diseases/depression-anxiety.html
-
4https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6065213/
Useful Links
Licensed by the State Department of Health Care Services.
Profound Healing Centers License No: 191092BP Exp. 5/31/26 (current/active)
Profound Healing Centers License No: 191092AP Exp. 7/31/25 (current/active)
Profound Treatment License No: 191047CP Exp. 1/31/27 (current/active)
Profound Treatment License No: 191047AP Exp. 8/31/26 (current/active)
Profound Treatment License No: 191047EP Exp: 3/31/26 (current/active)
Profound Treatment License No: 191047DP Exp. 9/30/25 (current/active)
Click here for more information about DHCS licensing.
| Start your healing today>> | |
|---|---|
| (310) 929-9546 |